Stress isn’t always a bad thing
It can give us extra energy for achievements, but if we face stress everyday it actually begins to change our brain. Find out more in this video

It can give us extra energy for achievements, but if we face stress everyday it actually begins to change our brain. Find out more in this video


What you eat could improve how your body responds to stress, according to experts. Introducing some new foods while cutting back on others may reduce the impact stress has on your body and day-to-day life. Here are four dietary changes designed to help you handle stress better.
As well as feeding you, the food you eat feeds the trillions of bacteria that live in your gut. Some studies find regulating gut bacteria via diet can have a positive impact on anxiety symptoms. The amount and types of bacteria in your gut are affected by your diet, and good dietary choices can “communicate calm to the brain”, according to Dr Rangan Chaterjee.
“The cheapest and simplest thing you can do to diversify and optimise the ‘good’ bacteria in your gut is to increase the variety of foods you eat…. Try to eat five different coloured vegetables every day”, says Dr Chaterjee. That’s because “minimally processed wholefoods – fibre” are best for your gut bacteria.
How does it work? The body cannot digest some fibre, including that found in many fruits and vegetables, so it’s fermented in the gut. Here it supports the growth of helpful microbes. As part of the fermentation process, the bacteria release essential chemicals and acids that interact with all the cells in your body. This interaction influences brain and immune health, according to Felice Jacka, Head of the Food and Mood Centre at Deakin University in Australia.
Jacka recommends eating foods from the Mediterranean diet, such as “fruit, vegetables, legumes and wholegrains, which all contain plant fibre”. She says fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, kombucha and kefir can nurture bacteria and yeasts in the gut, as well as being good for your wider health.

If your idea of dealing with stress is downing a pint of ice cream, you’re probably familiar with the concept of a ‘sugar high’, and possibly the ‘crash’ that comes afterwards. When you eat lots of sugar, your body releases insulin to absorb the excess glucose and regulate your blood-sugar levels. This journey of ups and downs may have negative side-effects, such as lack of concentration and tiredness, which can “hinder your ability to cope with stressful situations”, according to dietitian Sophie Medlin.

Positive and negative effects of caffeine on anxiety have been recorded. Most studies are based on research done with people already diagnosed with anxiety, but dietician Medlin says the results can often be applied to people suffering from everyday stress.
“The way you react may depend on your genetic sensitivity to caffeine, your gender and how much you drink, as well as existing anxious feelings”, says Medlin. Drinking caffeine can affect your sleep, which may impact the way you deal with stress. If drinking or eating caffeine negatively affects you, it’s a good idea to switch to decaf (although do this slowly, as caffeine withdrawals are no joke!).

“Never go into any stressful situation hungry… we’ve long recognised that hunger leads to irritability”, says Medlin. When you’re hungry, your blood sugar drops and your cortisol and adrenaline – those fight-or-flight hormones – rise. This is because the neuropeptides, secreted by neurons to control the chemicals in the brain, are the same for hunger as for anger. “Your body is pretty much still a caveman”, says Medlin. This explains why we often become irritable when peckish.
Adding ‘hanger’ to a stressful situation can enhance negative emotions. Have a few healthy snacks at hand to keep hunger pangs at bay, especially if you’re expecting a trying day.


“In 2015, 16.1 million Americans reported experiencing major depression during the previous year, often struggling to function while grappling with crippling darkness and despair.”
There’s an arsenal of treatments at hand, including talk therapy and antidepressant medications, but what’s depressing in itself is that they don’t work for every patient.
“Many people don’t respond to the frontline interventions,” said Benjamin Shapero, an instructor in psychiatry at Harvard Medical School (HMS) and a psychologist at Massachusetts General Hospital’s (MGH) Depression Clinical and Research Program. “Individual cognitive behavioral therapy is helpful for many people; antidepressant medications help many people. But it’s also the case that many people don’t benefit from them as well. There’s a great need for alternative approaches.”
Shapero is working with Gaëlle Desbordes, an instructor in radiology at HMS and a neuroscientist at MGH’s Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, to explore one alternative approach: mindfulness-based meditation.
In recent decades, public interest in mindfulness meditation has soared. Paralleling, and perhaps feeding, the growing popular acceptance has been rising scientific attention. The number of randomized controlled trials — the gold standard for clinical study — involving mindfulness has jumped from one in the period from 1995‒1997 to 11 from 2004‒2006, to a whopping 216 from 2013‒2015, according to a recent article summarizing scientific findings on the subject.
Studies have shown benefits against an array of conditions both physical and mental, including irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, psoriasis, anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder. But some of those findings have been called into question because studies had small sample sizes or problematic experimental designs. Still, there are a handful of key areas — including depression, chronic pain, and anxiety — in which well-designed, well-run studies have shown benefits for patients engaging in a mindfulness meditation program, with effects similar to other existing treatments.
“There are a few applications where the evidence is believable. But the effects are by no means earth-shattering,” Desbordes said. “We’re talking about moderate effect size, on par with other treatments, not better. And then there’s a bunch of other things under study with preliminary evidence that is encouraging but by no means conclusive. I think that’s where it’s at. I’m not sure that is exactly how the public understands it at this point.”
Desbordes’ interest in the topic stems from personal experience. She began meditating as a graduate student in computational neuroscience at Boston University, seeking respite from the stress and frustration of academic life. Her experience convinced her that something real was happening to her and prompted her to study the subject more closely, in hopes of shedding enough light to underpin therapy that might help others.
“My own interest comes from having practiced those [meditation techniques] and found them beneficial, personally. Then, being a scientist, asking ‘How does this work? What is this doing to me?’ and wanting to understand the mechanisms to see if it can help others,” Desbordes said. “If we want that to become a therapy or something offered in the community, we need to demonstrate [its benefits] scientifically.”
Desbordes’ research uses functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), which not only takes pictures of the brain, as a regular MRI does, but also records brain activity occurring during the scan. In 2012, she demonstrated that changes in brain activity in subjects who have learned to meditate hold steady even when they’re not meditating. Desbordes took before-and-after scans of subjects who learned to meditate over the course of two months. She scanned them not while they were meditating, but while they were performing everyday tasks. The scans still detected changes in the subjects’ brain activation patterns from the beginning to the end of the study, the first time such a change — in a part of the brain called the amygdala — had been detected.
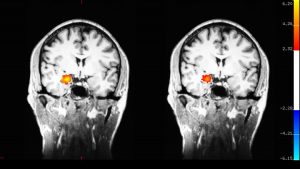
Functional MRI (left) showing activation in the amygdala when participants were watching images with emotional content before learning meditation. After eight weeks of training in mindful attention meditation (right) note the amygdala is less activated after the meditation training. Courtesy of Gaelle Desbordes
In her current work, she is exploring meditation’s effects on the brains of clinically depressed patients, a group for whom studies have shown meditation to be effective. Working with patients selected and screened by Shapero, Desbordes is performing functional magnetic resonance imaging scans before and after an eight-week course in mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, or MBCT.
During the scans, participants complete two tests, one that encourages them to become more aware of their bodies by focusing on their heartbeats (an exercise related to mindfulness meditation), and the other asking them to reflect on phrases common in the self-chatter of depressed patients, such as “I am such a loser,” or “I can’t go on.” After a series of such comments, the participants are asked to stop ruminating on the phrases and the thoughts they trigger. Researchers will measure how quickly subjects can disengage from negative thoughts, typically a difficult task for the depressed.
The process will be repeated for a control group that undergoes muscle relaxation training and depression education instead of MBCT. While it’s possible that patients in the control part of the study also will have reduced depressive symptoms, Desbordes said it should occur via different mechanisms in the brain, a difference that may be revealed by the scans. The work, which received funding from the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, has been underway since 2014 and is expected to last into 2019.
Desbordes said she wants to test one prevalent hypothesis about how MBCT works in depressed patients: that the training boosts body awareness in the moment, called interoception, which, by focusing their attention on the here and now, arms participants to break the cycle of self-rumination.
“We know those brain systems involved with interoception, and we know those involved with rumination and depression. I want to test, after taking MBCT, whether we see changes in these networks, particularly in tasks specifically engaging them,” Desbordes said.
Desbordes is part of a community of researchers at Harvard and its affiliated institutions that in recent decades has been teasing out whether and how meditation works.
In the 1970s, when transcendental meditation surged in popularity, Herbert Benson, a professor at Harvard Medical School and what was then Beth Israel Hospital, explored what he called “The Relaxation Response,” identifying it as the common, functional attribute of transcendental meditation, yoga, and other forms of meditation, including deep religious prayer. Benson described this response — which recent investigators say is not as common as he originally thought — as the opposite of the body’s adrenalin-charged “fight or flight” response, which was also identified at Harvard, by physiologist Walter Cannon Bradford in 1915.
Other MGH researchers also are studying the effects of meditation on the body, including Sara Lazar, who in 2012 used fMRI to show that the brains of subjects thickened after an eight-week meditation course. Work is ongoing at MGH’s Benson-Henry Institute; at HMS and Brigham and Women’s Hospital’s Osher Center for Integrative Medicine; at the Harvard-affiliated Cambridge Health Alliance, where Zev Schuman-Olivier directs the Center for Mindfulness and Compassion; and among a group of nearly a dozen investigators at Harvard and other Northeastern institutions, including Desbordes and Lazar, who are collaborating through the Mindfulness Research Collaborative.
Among the challenges researchers face is defining mindfulness itself. The word has come to describe a meditation-based practice whose aim is to increase one’s sense of being in the present, but it has also been used to describe a nonmeditative state in which subjects set aside their mental distractions to pay greater attention to the here and now, as in the work of Harvard psychologist Ellen Langer.
Another challenge involves sorting through the many variations of meditative practice.
Recent scientific exploration has largely focused on the secular practice of mindful meditation, but meditation is also a component of several ancient religious traditions, with variations. Even within the community practicing secular mindful meditation, there are variations that may be scientifically meaningful, such as how often one meditates and how long the sessions are. Desbordes herself has an interest in a variation called compassion meditation, whose aim is to increase caring for those around us.
Amid this variation, an eight-week mindfulness-based stress reduction course developed in the 1970s by Jon Kabat-Zinn at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center has become something of a clinical and scientific standard. The course involves weekly two- or 2½-hour group training sessions, 45 minutes of daily work on one’s own, and a daylong retreat. The mindfulness-based cognitive therapy used in Desbordes’ current work is a variation on that program and incorporates elements of cognitive behavioral therapy, which involves talk therapy effective in treating depression.
Ultimately, Desbordes said she’s interested in teasing out just what in mindful meditation can work against depression. If researchers can identify what elements are effective, the therapy may be refined to be more successful. Shapero is also interested in using the study to refine treatment. Since some patients benefit from mindfulness meditation and some do not, he’d like to better understand how to differentiate between the two.
“Once we know which ingredients are successful, we can do more of that and less, maybe, of the parts that are less effective,” Desbordes said.
Research funding includes the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health.